Getting Started
MIDAS is an exploratory data analysis tool that runs in your browser. No installation required - start analyzing right away.
Tutorial: Exploratory Data Analysis with the Iris Dataset
1. Open Sample Data
- When you open MIDAS, the launcher screen appears
- Click Iris dataset from the "Sample Data" section
- The project screen opens
The Iris dataset contains measurements of petals and sepals from three species of iris flowers (150 rows × 5 columns).
2. Explore the Data
Three tabs open automatically:
- Data Table (left): Displays data in tabular format
- Statistics (top right): Shows statistics for the entire dataset
- Selected Rows (bottom right): Details of selected rows
View Live Demo
Click to launch the MIDAS application
Each column header shows the data type (float64, string, etc.) and measurement scale (interval, nominal, etc.). Click the button at the right edge of a column to sort by that column.
MIDAS automatically infers data types and measurement scales when loading data. Measurement scales play an important role in statistical analysis and graph creation. See Data Preparation and Import for details.
3. View Basic Statistics
Let's check basic statistics to understand the data overview.
- Click a column name in the Data Table tab (e.g.,
sepal_length) - Statistics automatically appear in the Statistics tab on the upper right
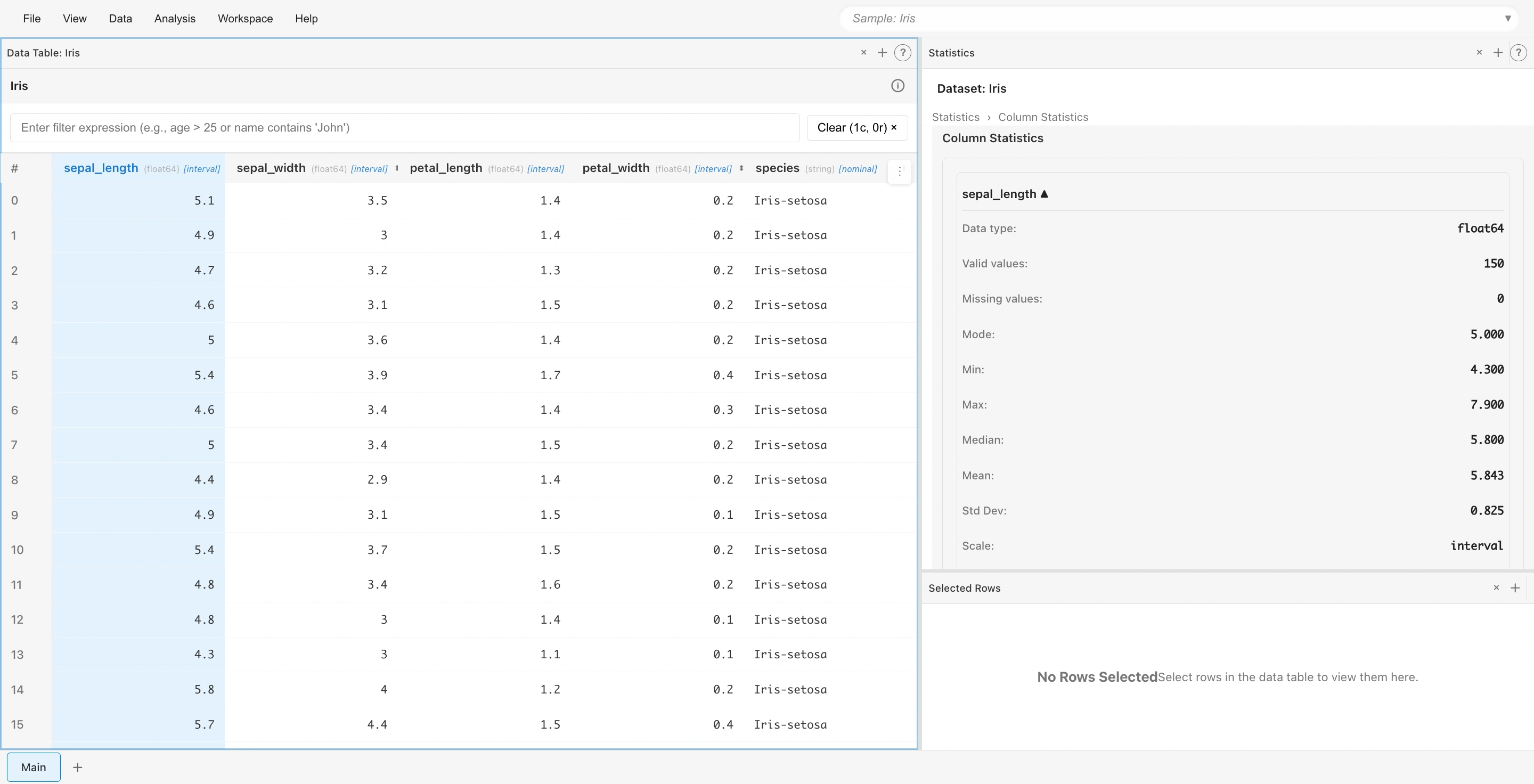
Statistics displayed:
- Valid values: Number of valid data points
- Missing values: Number of missing values
- Mode: Most frequent value
- Min: Minimum value
- Max: Maximum value
- Median: Median value
- Mean: Average value
- Std Dev: Standard deviation
A histogram and density curve are also displayed, allowing you to visually confirm the data distribution.
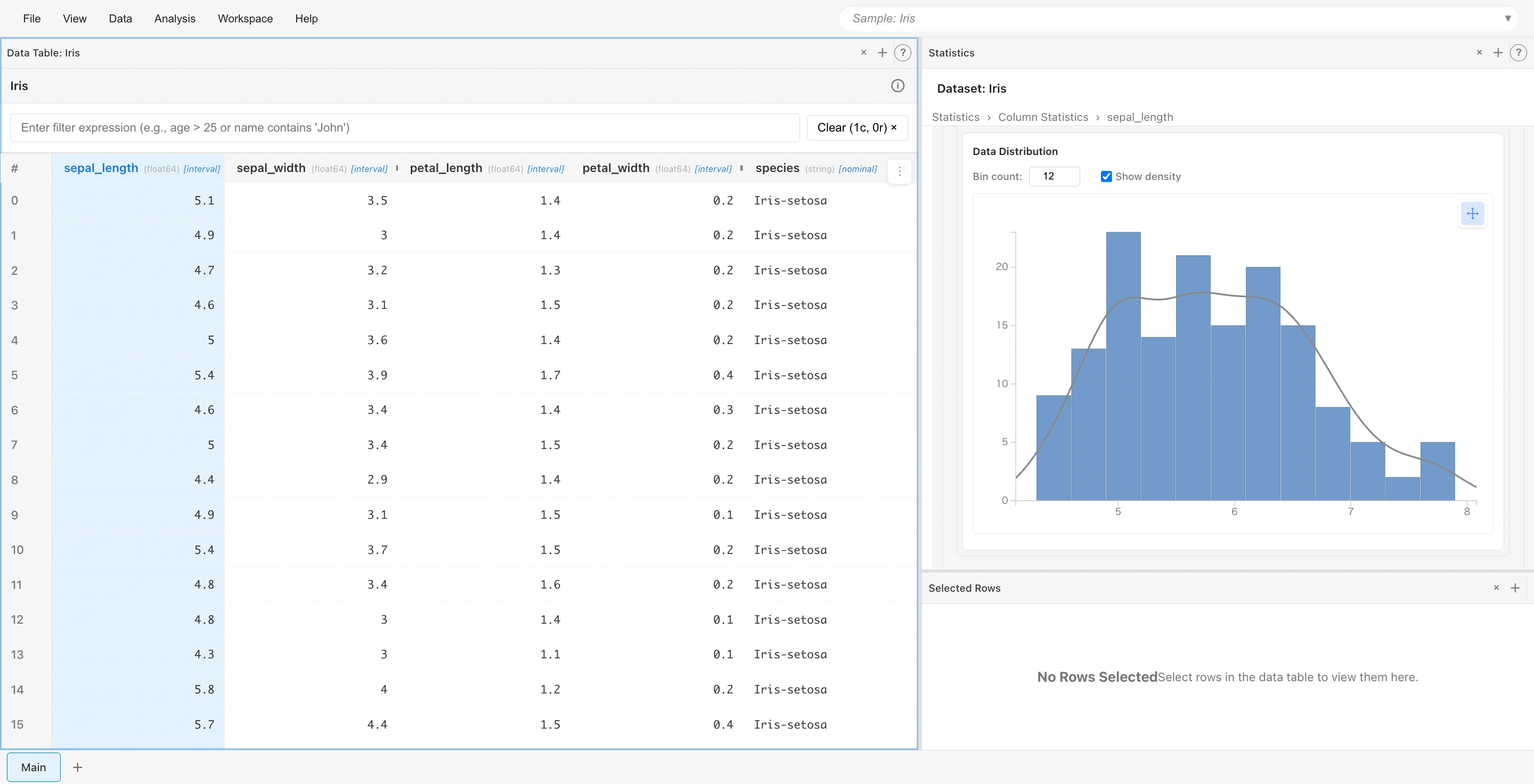
Select rows from histogram:
Click a bar in the histogram to select rows within that range. Details appear in the Selected Rows tab at the bottom right.
You can examine selected row data in detail or analyze only data within a specific range.
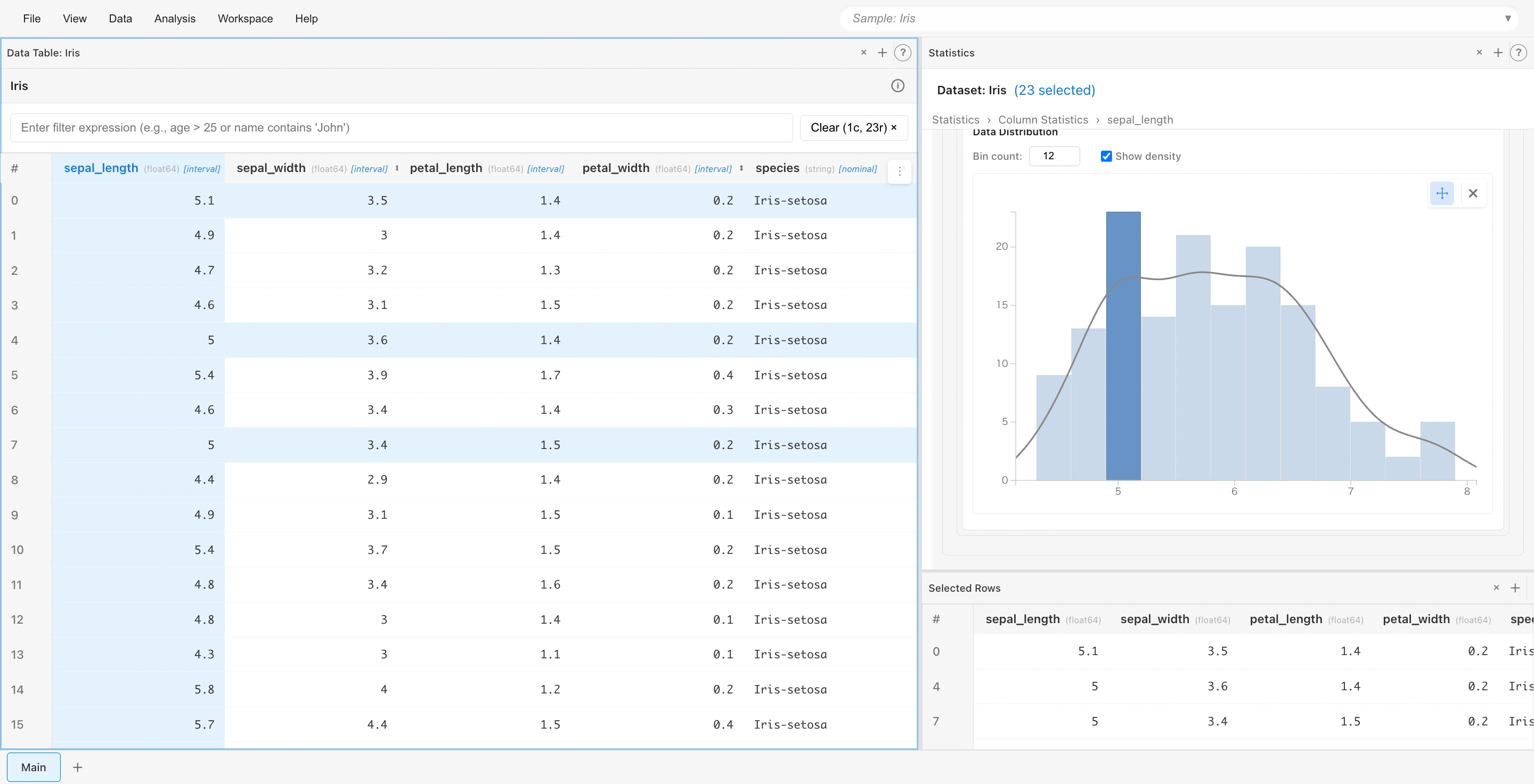
Select two columns to display a scatter plot:
- With
sepal_lengthselected, Ctrl/Cmd+clicksepal_width - Scroll the Statistics tab to see a scatter plot of the two columns
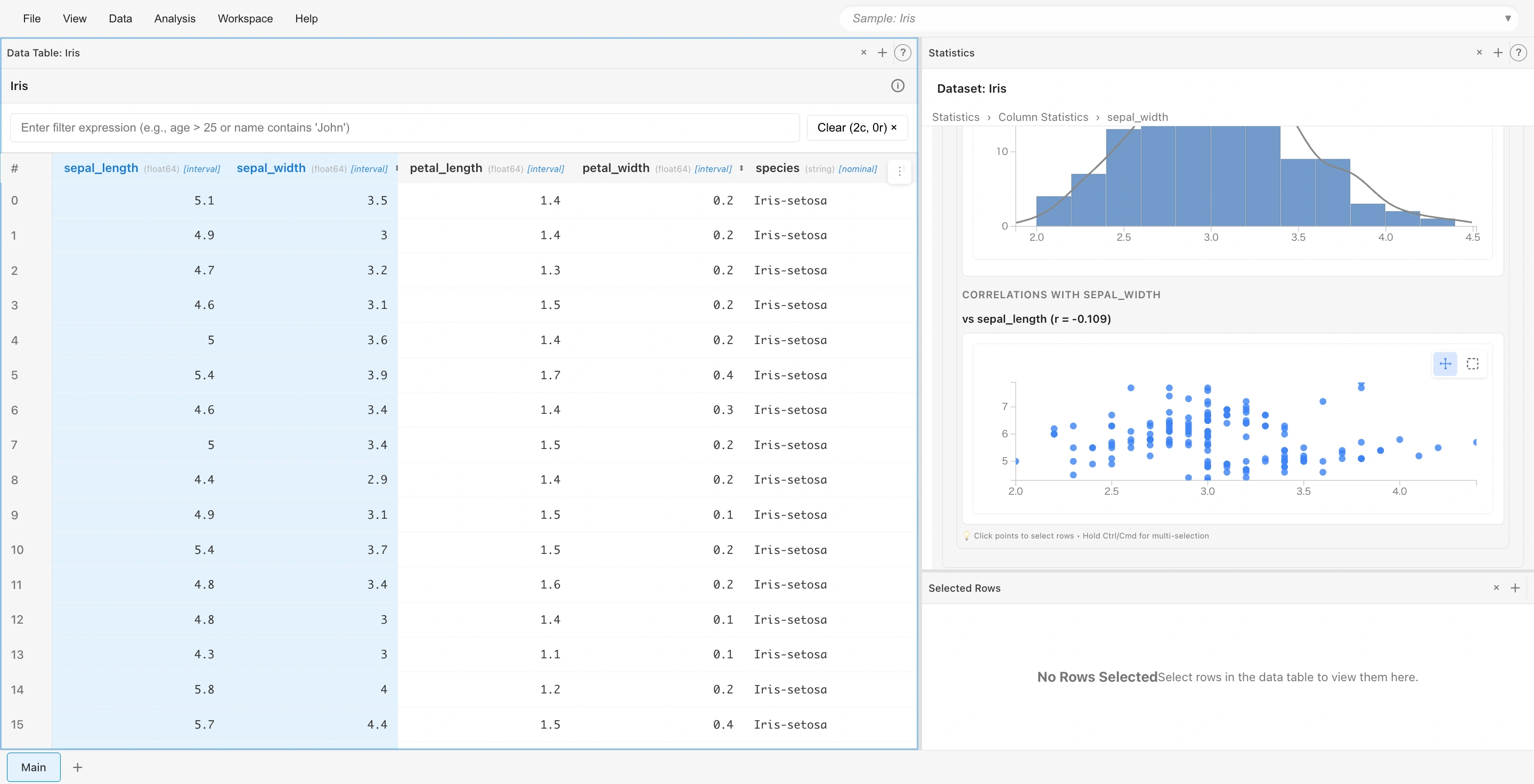
The correlation coefficient (r value) is also displayed.
4. Create Graphs
Let's visualize the data to discover patterns.
Create a Scatter Plot
- Select Analysis → Graph Builder... from the menu bar
- Click the Scatter Plot button
- Select from the dropdowns:
- X-Axis:
sepal_length (interval)(sepal length) - Y-Axis:
sepal_width (interval)(sepal width) - Color (Optional):
species (nominal)(iris species)
- X-Axis:
- A scatter plot appears, color-coded by species
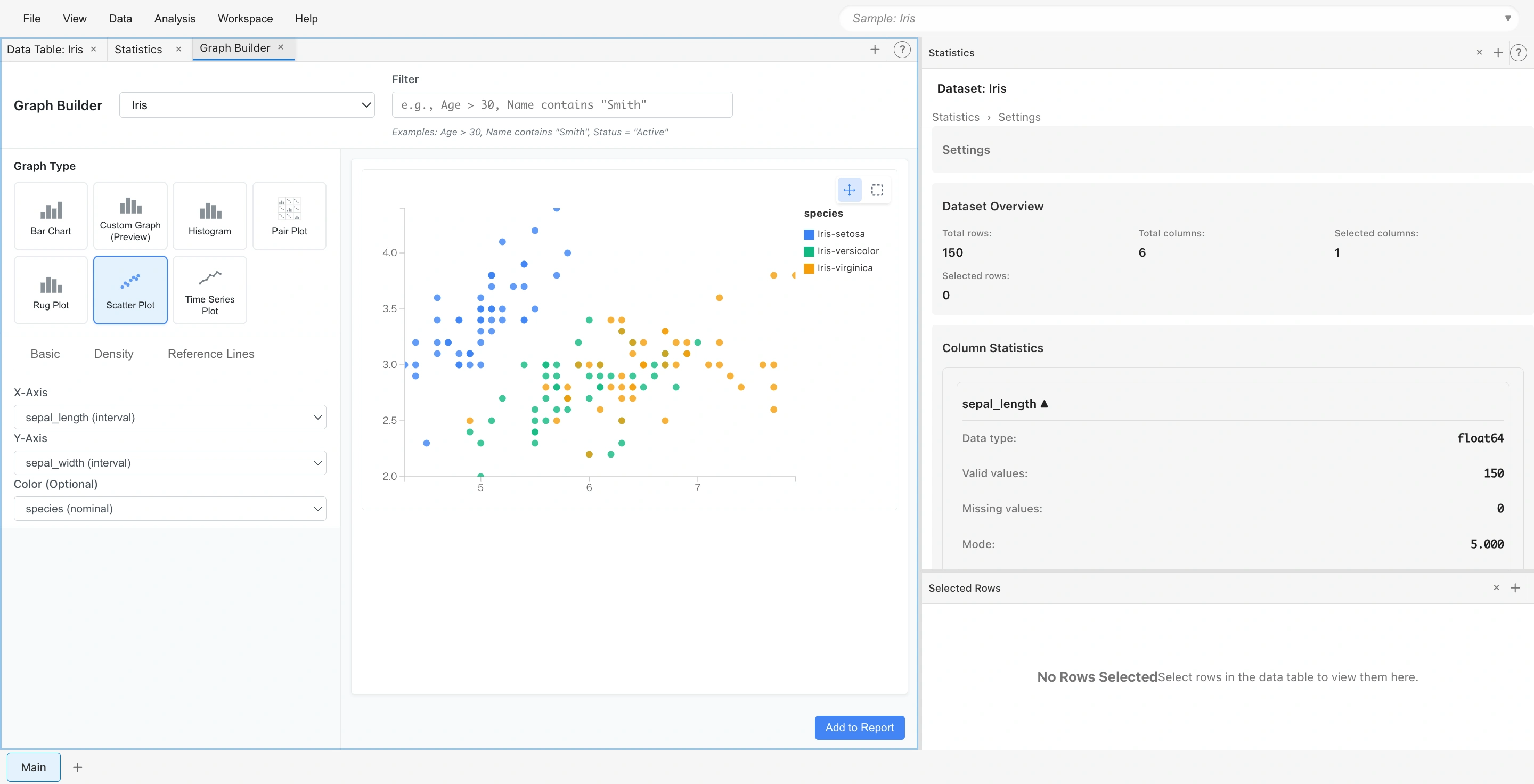
You can see that data clusters in different regions for each species.
See Creating Graphs and Advanced Graph Creation for more details.
5. Save Your Project
MIDAS offers two ways to save your work.
Save to Browser
- Select File → Save to Browser (or Ctrl/Cmd+S)
- The project is automatically saved to your browser
Next time you open MIDAS, saved projects appear in the "Quick Access" section of the launcher screen for quick resumption.
Export as File
- Select File → Export Project... (or Ctrl/Cmd+Shift+S)
- Confirm or edit the filename (defaults to project name)
- Click Save
- A project file (.mds format) is downloaded
Open an Exported File
- In the MIDAS launcher screen, click Choose File in the "Open Project File" section
- Select a saved
.mdsfile - The project loads and restores to its saved state
Related Pages
- Sample Datasets - Other sample data included in MIDAS
- Data Preparation and Import - File formats, data types, and measurement scales
- Creating Graphs - How to use various graph types
- Advanced Graph Creation - Flexible visualization with Grammar of Graphics